Difference Between Symbiosis and Mutualism
Survival is one of the foremost instincts of all the species in this world. Organisms such as plants adopt different ways of ensuring this survival.
After doing an intensive research on different organisms, biologists have discovered that in order to survive and maintain a healthy growth, some organisms form a relation or an association with other organisms. The nature of these associations varies, though they can all be categorised as symbiosis.
Symbiotic associations can be of three kinds, namely commensalism, parasitism and mutualism. While talking about mutualism, a lot of people find themselves struggling to differentiate between symbiosis and mutualism.
The confusion is understandable because both the words are indeed related. However, the relation is based on the fact that mutualism is a sub-category of symbiosis. What this basically means is that while all mutual relationships are symbiotic relationships, the same does not hold true for all symbiotic relationships. Some of them can be mutual relationships, while some do not.
Another thing that needs to be taken note of is the fact that symbiosis views the associations between two or more organisms that live together in a broader spectrum, whereas mutualism is a part of this spectrum, describing an association in which the parties involved in the association benefit from each other.
Instructions
-
1
Symbiosis
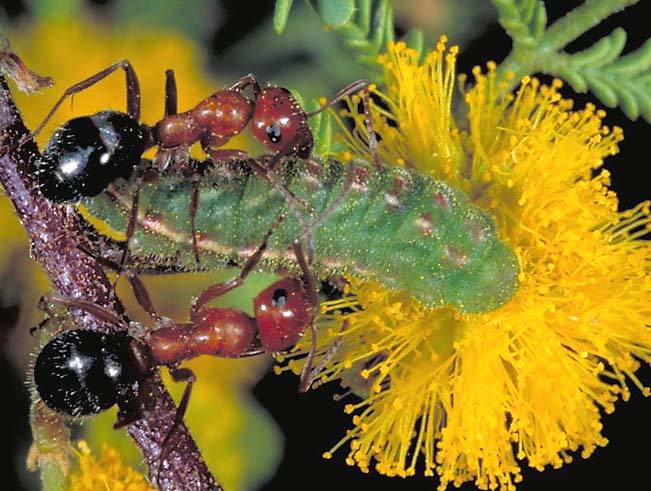
In the most simplest of terms, symbiosis can be described as a close and typically long-term association between two or more different biological species. The different types of symbiotic associations, namely commensalism, parasitism and mutualism, describe the nature of the relationship between the species. In commensalism, only one party is benefited from the association, whereas no harm is done to the other party. In parasitism, one party benefits from the association, while the other party is damaged or harmed. The party benefiting from the association is known as the parasite, whereas the party that is being harmed is known as the host. In some cases, the parasite damages the host only partially while using it to obtain important nutrients and water for survival. However, in some cases, the parasite continues to damage the tissues of the host until the latter dies. The parasite and then moves on to another specie to build another parasitic association with it and thus ensure its survival.
Image Courtesy: redbubble.com
-
2
Mutualism
Mutualism is described as a relation between two or more biological species in which all the parties benefit from the association. This kind of association is pretty common between plants and fungus.
Image Courtesy: dimijianimages.com







