What is a Lobotomy and Why Were They Conducted
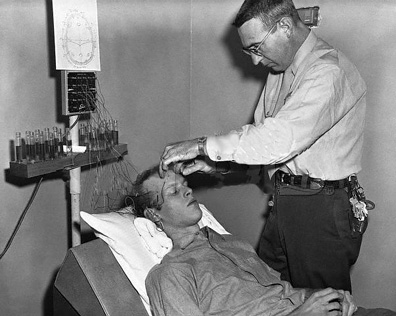
Lobotomy is known as a neurosurgical procedure, which can also be considered as a form of psychosurgery.
This medical procedure involves cutting away most of the neural connections to the prefrontal cortex or anterior part of the brain. The procedure has been controversial since it started in 1935.
After the founder of this procedure, António Egas Moniz, received the Nobel Prize for Physiology in 1949, the use of this procedure soared. By 1951, around 20,000 procedures were performed in the United States alone. As antipsychotic medications improved in the late 1950’s, the lobotomy was not used by mental health professionals.
Instructions
-
1
When the number of mental patients in hospitals increased drastically in the early 20th century, there was a need for developing some sort of medical treatment for this problem as none existed at the time. It was then that Lobotomy was introduced as an invasive physical therapy in parts of Europe. Some of the other therapies during this era include, malarial therapy for general paresis of the insane (1917), deep sleep therapy (1920), insulin shock therapy (1933), cardiazol shock therapy (1934) and electroconvulsive therapy (1938). It was in fact the success of shock therapy which helped doctors carry out procedures such as lobotomies.
-
2
According to documented records, some 40,000 people in the United States were lobotomised. In Great Britain 17,000 while three Nordic countries of Norway, Sweden and Finland had a combined number of 9,300 lobotomy procedures. It is estimated that in Sweden almost 4,500 people were lobotomised from 1944 to 1966, which mainly included women. In Norway there were 2,500 reported cases, while in Denmark, there were 4,500 lobotomies. However, by the 1970's this procedure was stopped.
-
3
The problem with this procedure is that it can have an adverse effect on a patient's personality and capacity of working independently. Most times, a reduction in initiative and inhibition is observed in the patients after the procedure. They also exhibit detachment from society, making it quite difficult for a patient to socialise and return to normal life.
-
4
While this procedure has faced severe criticism, National Committee for the Protection of Human Subjects of Biomedical and Behavioral Research, created by the US Congress in 1977, concluded that some properly performed psychosurgery can produce positive effects.
-
5
In this modern time a lobotomy is considered to be a cruel and painful procedure for helping a patient with severe mental illness. New techniques and medication has allowed for a better understanding and improved methods for treating mental health issues.




