Difference Between Esophagus and Trachea
Trachea and esophagus are two different organs present in almost every animal. The basic difference between esophagus and trachea is that the former forms part of the digestive system of a living organism whereas the latter is a part of the respiratory system. Being parts of different systems, both trachea and esophagus perform different functions.
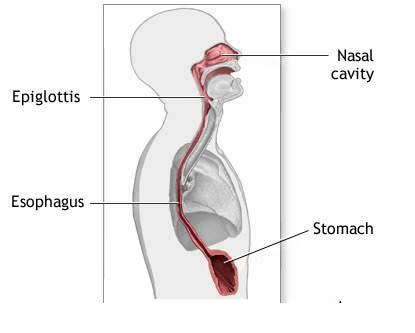
Along with their functions, they both differ in their structures as well. Trachea is a strong and wide cartilaginous tube that helps take air to and from bronchi. It makes an important part of the respiratory system of all the living organisms that breath in through lungs. Esophagus on the other hand, is a long and flexible structure that connects your mouth to your stomach. The food that you eat goes from your mouth into the stomach cavity as a result of the muscular movements of the esophagus.
Since the trachea is responsible for transporting oxygen to the lungs, it is crucial that it remains open and clear all the time. Even an invisible dust particle can cause irritation in the wind pipe, resulting in severe cough.
Both trachea and esophagus are roughly located close to each other, positioned in a way that the latter lies on the posterior side of the former. A tiny flap, called epiglottis, present at the top of the trachea, separates these two tubes. The epiglottis keeps food particles from entering the respiratory track as you swallow them.
Several cartilaginous semi circular rings join together to form the trachea, whereas the esophagus is a muscular tube. The trachea’s length ranges from 9 to 15 centimetres, while an esophagus is usually ten inches long. Moreover, the trachea only has thoracic and cervical parts, whereas an esophagus’ structure is divided into three parts – cervical, thoracic and abdominal.
Furthermore, the trachea is a stiff, straight tube, while the esophagus is surprisingly flexible and can swallow almost everything. Another important difference between trachea and esophagus can be seen in their blood supplies. The former gets its blood supply from the lower thyroid arteries while the arteries in the thorax and abdominal region supply blood to the latter.
Instructions
-
1
Trachea
Trachea is an anatomical structure present in both vertibrates and invertibrates, which they use to breathe. Also called the wind pipe, trachea is a strong, wide tube, that transports oxygen to the lungs and removes carbon dioxide.
Image courtesy: wisegeek.com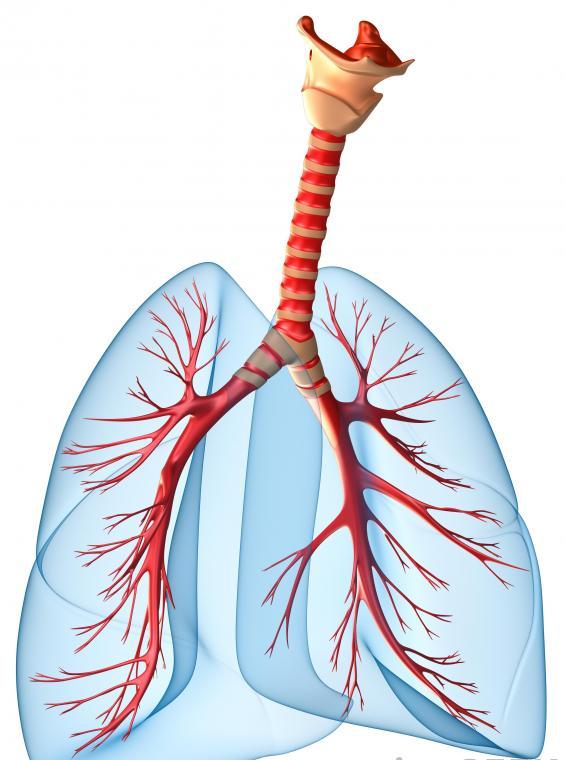
-
2
Esophagus
The esophagus is an important part present in all vertebrates, which connects the pharynx with the stomach. It is a muscular tube that uses mechanical movements to pass food from the mouth to the stomach.
Image courtesy: scripps.org