Difference between Actin and Myosin

A lot of individual spend hours in the gym to build muscles. It is certainly a gruelling activity, therefore only some succeed to become giant body builders. If someone is interested in getting the best results within a short period of time, he/she first of all needs to know the composition of the muscles.
You will find both Actin and Myosin in the muscles. Both function only for the contraction of the muscles in the presence of the calcium ions. Although the job is very similar, there is a significant difference between these two protein filaments.
Actin and myosin are basically the striations in skeletal muscles, and the major difference between them is the size. Also known as the ‘I Band’, the actin filaments are very thin. And on the other hand, the thicker filaments are referred as Myosin.
The troponin-tropomyosin-actin complex is responsible to block actin’s attachment to myosin. There is a mighty different between their structures. An Actin filament consists of only strands, whereas the myosin filament is a combination of bundles of molecules.
The end result is muscle contraction, but both filaments have different jobs to do. Their function is thoroughly described by the sliding filament theory. Both filaments are responsible for the cellular movements, having no role to play in the non-cellular movements.
Calcium ions are the basic requirement for the muscles contraction. The process consists of a couple of steps. The first action is to stimulate SR to release the calcium ions, while the second action is about re-absorbtion of the calcium back to the SR area.
Instructions
-
1
Actin
An actin filament is actually a combination of a couple of actin strands. They are very light as compared to the myosin filaments. These filaments play a crucial role when the calcium present deep into the muscles re-absorbs after its release during the muscle contraction.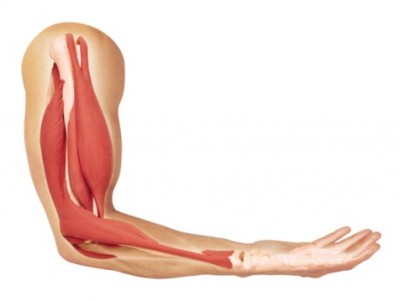
-
2
Myosin
Myosin filaments are totally responsible for H zone - the dark bands or striations. The A band is referred as the length of filament, whereas the central thickening is called as the M line. Since these filaments also play a major role in converting ATP to ADP, they are also called as myosin enzymes.