Difference Between Electronegativity and Electron Affinity
Electron affinity and electronegativity are two terms used to describe the tendency of an atom to form a bond with another atom. Electron affinity is the amount of energy released when an electron is a added to or removed from an atom, whereas Electronegativity is the tendency of an atom to attract more electrons towards itself.
Electron affinity is quantifiable, which means its value can be easily calculated by finding the energy released when an electron is detached from an isolated gaseous atom to convert it to a positively charged ion. Electronegativity on the other hand, is not a quantitative concept and is used to explain the making of covalent bonds and the polarity of atoms making the covalent bond.
Electronegativity defines the location of the bonded pair of electrons in a covalent compound. The shared pair of electrons is localized more towards the atom which is more electronegative, inducing a partial negative charge on that atom and a partial positive charge on the less electronegative atom.
Electron affinity deals with a single, neutral atom, while electron affinity deals with atoms in a chemical compound. In simple words, the former is a concept related to a single atom while the latter deals with atoms in a molecule. Electron affinity is a concept related to formation of ionic compounds, in which electrons transfer completely from one atom to the other, whereas Electronegativity is related to covalent bond formation, in which electrons are shared between two atoms.
Moreover, electron affinity is the measurement of a specific characteristic whereas Electronegativity is a property.
Instructions
-
1
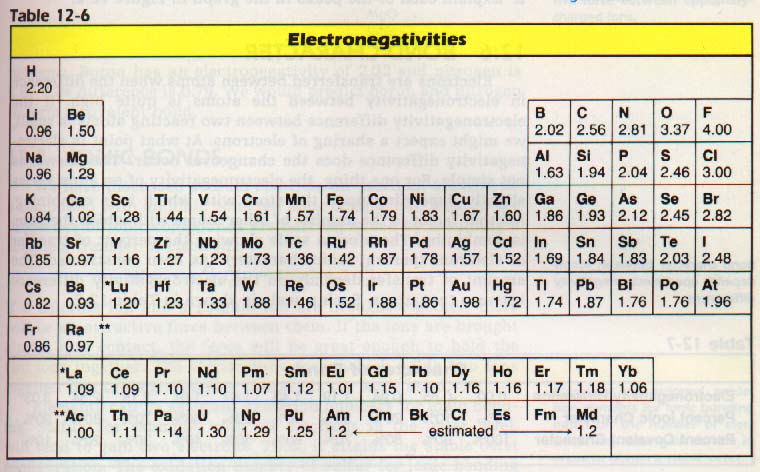
Electronegativity
Electronegativity is a chemical property that describes the tendency of an atom or a functional group to attract a shared pair of electrons towards itself. The Electronegativity of an atom depends upon its atomic number (number of protons in nucleus) as well as the distance of the valence shell electrons from the nucleus. The greater the atomic number of an atom the more pull it will have on negatively charged electrons.
Flourine is the most electronegative element in the periodic table, whereas caesium is the least electronegative element. Electronegativity increases as we move from left to right and decreases from top to bottom on the periodic table.
Image courtesy: chemwiki.ucdavis.edu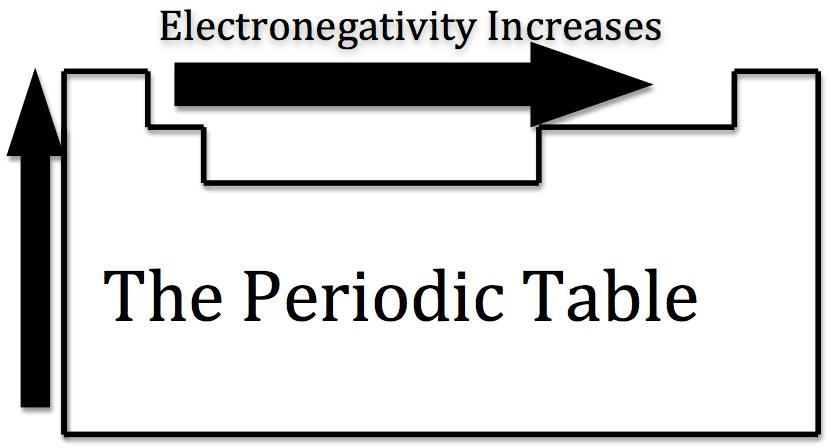
-
2
Electron affinity
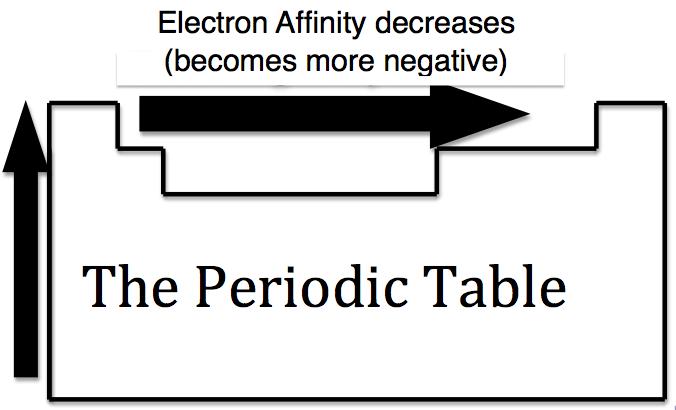
Electron affinity of an atom or molecule is defined as the amount of energy released when an electron is added to an isolated gaseous atom or molecule to form a negative ion. Electron affinity increases from left to right and decreases from top to bottom in the periodic table.
Image courtesy: chemwiki.ucdavis.edu