Difference between Euglena and Paramecium
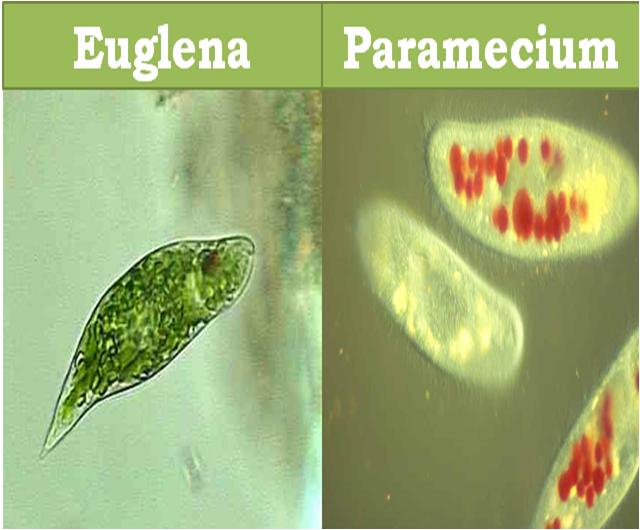
Euglena and Paramecium are both uni-cellular microscopic organisms but differ from one another in body structure, way they move, feeding modes and many other aspects. It is important for everyone, especially science and botany students, to thoroughly understand each and every difference between Euglena and Paramecium.
Euglena is a flagellate creature with one whip-like organelle called as flagella. Paramecium, on the other hand is a ciliate – organism with hair-like organelles called cilia.
Related : How to Get Rid Of Allergies
Instructions
-
1
Euglena exhibits both plant and animal characteristics, whereas paramecium possesses only animal features.
Euglena reproduces asexually, while paramecium reproduces both sexually and asexually.
Euglena contains chloroplast, a plastid that contains chlorophyll. Paramecium, on the contrary, does not possess chloroplast.
Paramecium is a heterotroph, an organism that obtains its food directly from organic carbon. Euglena is a heterotroph and an autotroph, an organism that produces its own food through chemosynthesis or photosynthesis.
Euglena possesses the capability to stay alive during long droughts without water or light, but Paramecium cannot survive for long in such conditions.
Euglena is a flexible creature as its skin and membrane is made up of pellicle, unlike paramecium. -
2
Euglena
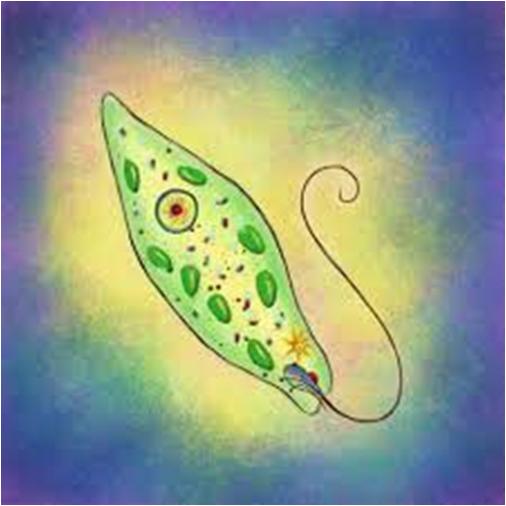
Euglena is a broadly studied single-celled genus of phylum Euglenozoa. There are around 44 genera and 800 species in this phylum. It is pear shaped and green in color.
Euglena prefers freshwater, but some of the species are found in saltwater. This interesting organism acts an animal or plant. For example, it contains chlorophyll and therefore can make its own food like plants. When away from light, however, it can get food like an animal, ingesting tiny creatures.
Its whippy tail (flagellum) helps it to move through the water while it’s bright red eyespot assist in finding light. It reproduces by fission, ripping lengthwise in two equal halves.
Under too hot or cold conditions, euglena forms a defensive coat called a cyst around its body that protects it until the external conditions become normal.
-
3
Paramecium
Paramecium is the name of microscopic genus of the phylum Ciliophora. This slipper shaped organism is usually 70 to 140 um in length. It is common in freshwater, salty and oxygenated aquatic environments, and is often very abundant in stagnant ponds and basins.
It is known for its “avoidance behavior.” Whenever it comes across an unsafe stimulus, it has the ability to revolving up to approximately 360 degrees to find an escape direction. Its rigid, yet stretchy pellicle membrane helps in maintaining definite shape. Paramecium feeds on other microscopic organisms, including yeast cells, algae and bacteria etc.