Difference between Jejunum and Ileum
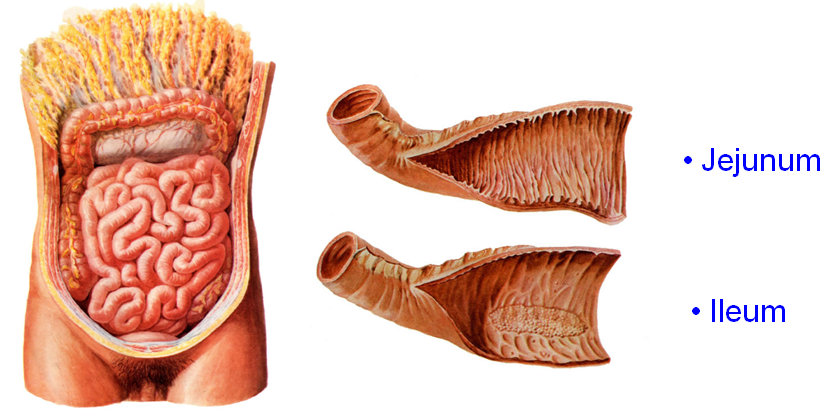
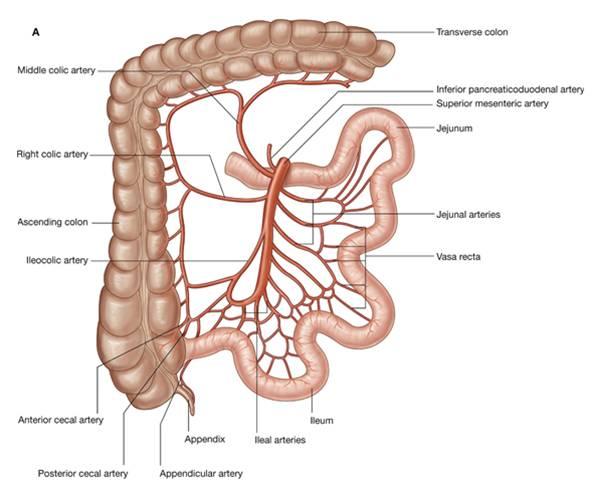
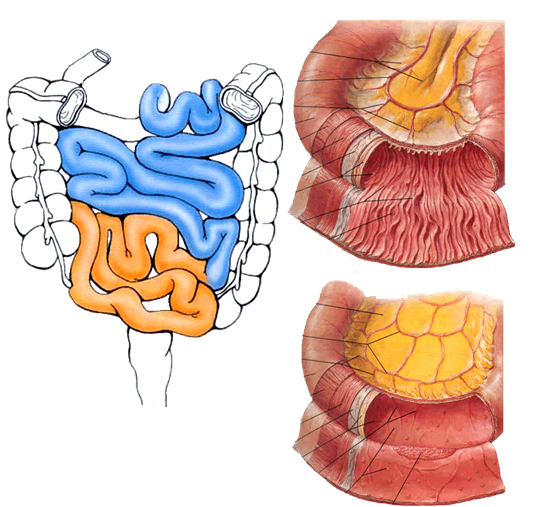
The small intestine makes the entire bowel system in the human body, and is further divided into three distinctive parts, including the duodenum, the jejunum and the ileum. In order of occurrence, the jejunum refers to the second or middle part of the small intestine while the ileum is the innermost part of the small intestine, lying just before the rectum or the large intestine. The length of the small intestine in adult humans is usually between 5.5 to 6 meters. About 3.5 to 4 meters of which is the ileum, and 2.5 meters is the jejunum, which shows that the ileum is the lengthiest part of the small intestine, starting from the jejunum, leading all the way to the ileocecal valve, where it joins with the large intestine.
Apart from lengths, both these parts differ in their functions as well. Jejunum is the part of the human digestive system where various processes of digestion and secretion of enzymes take place. Moreover, the absorption of components like glucose, fat and amino acids from the digested food also begins in the jejunum. Ileum, on the other hand, is the site for the digestion and absorption of vitamin B complex. Coupled bile salts that do not get absorbed in jejunum are also absorbed in the ileum.
The composition of ileum and jejunum is also different. The former contains huge quantities of Mucosa Associated Lymph Tissue in the structure of Peyer’s patches, while the latter contains minor traces of the MALT elements. Furthermore, the Ileum contains a large number of arterial arcades and arteriae recta as compared to the jejunum. The size of the arterial arcades found in the former is also much smaller than those found in the latter.
During the split open small intestine transplantation, jejunum is more likely to have a successful surgery as compared to the ileum.
Instructions
-
1
Jejunum
Jejunum refers to the middle section of the small intestine in higher vertebrates, lying towards one side of the duodenum. Middle intestine or mid-gut are the other two terms used to describe jejunum. The pH of the enzymes in the jejunum ranges from 7 to 9, which indicates a neutral or slightly alkaline medium.
Image courtesy: medicinembbs.blogspot.com
-
2
Ileum
Ileum is the last part of the small intestine which joins the small intestine in higher vertebrates to the large intestine. The pH in ileum is between 7 and 8. The ileum has more fat inside the mesentery than the jejunum. The basic function of ileum is to absorb vitamin B12, however, it also absorbs the digested contents that were not absorbed by the jejunum.
Image courtesy: studyblue.com