Difference between Lacquer and Varnish

Lacquer and Varnish are both wood finishes applied to furniture, wooden floors and outdoor items in order to improve their appearance as well as protect them from the effects of weathering. While they both serve the same purpose, they differ from each other in terms of their compositions and modes of application.
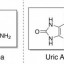
Lacquer mainly consists of a fast drying resin which is prepared from celluloid objects called nitrocellulose. Cotton is the major source of the resin used to prepare lacquer. Varnish on the other hand, includes oils and solvents in addition to resin. The difference in composition means varnish dries up to form a protective layer over the surface it has been applied to, whereas lacquer melts into the paint layer underneath to provide a very hard yet flexible finish.
Lacquer however, is more volatile than varnish and this is the reason why it is often sprayed, as opposed to being applied with a brush. While the former can be applied to both wood and metal, the latter can only be applied to wooden structures and does not adhere to metals. Varnish is usually brushed onto the wood, unlike lacquer.
Furthermore, only one coat of lacquer suffices most of the time, but in case of varnish, several coats are applied to get a strong and durable finish.
Instructions
-
1
Varnish
Varnish is a common wood finish that makes the surface underneath resistant to heat, moisture and several solvents. It is created from a resin, usually alkyd or polyurethane, dissolved in a solvent with drying oil. Specific oil types, such as linseed oil, soybean oil or tung oil are used to dissolve the resin in a bid to cure it when exposed to air.
Varnish is usually clear and is mostly applied to untreated wood or wood that has been stained. As it dries, the varnish forms a protective layer over the wooden structure it has been applied to, giving it additional protection.
Image courtesy: thewoodflooringspecialist.co.uk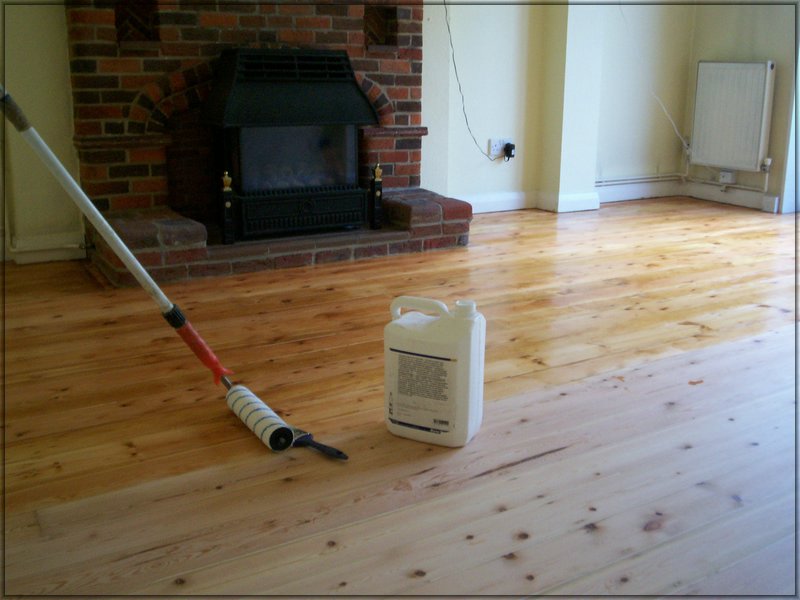
-
2
Lacquer
Lacquer is a clear nitrocellulose dissolved in a fast drying solvent. It is applied to wooden furniture, floors and other structures to create a clear protective film over them, while allowing the beauty of the wood underneath to show through. There are also lacquers that are stained with pigment.
Lacquer does not adhere to formerly polyurethaned or varnished finish. It provides a really hard finish that makes the wood underneath resistant to damage from moisture, alkalies and acids.
Image courtesy: floanderson.com