Difference Between Taxonomy and Systematics

Taxonomy and systematics are often used synonymously which is totally incorrect. Although, both the terms are related to the biological study of living organisms, there is a considerable difference between the two.
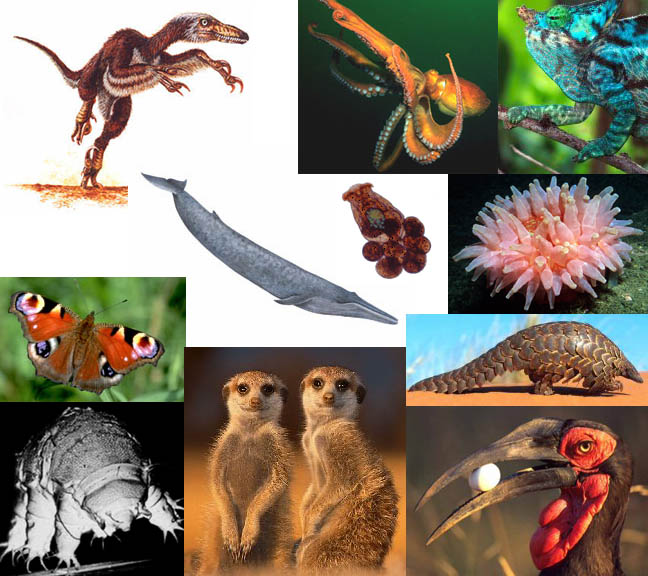
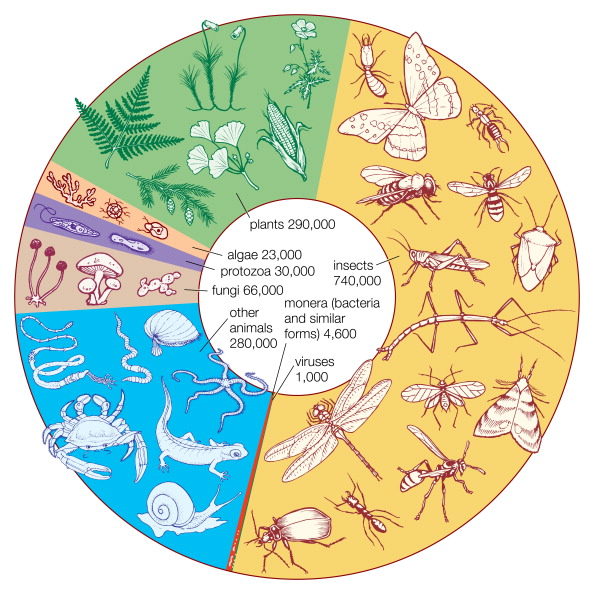
Taxonomy refers to a study which helps to organise the living organisms into different groups according to their physical characteristics and other traits. On the other hand, systematics is the study of the evolution of living things through time. The process of evolution in systematics is studied with the help of phylogenetic trees which are created with the help of taxonomy.
Instructions
-
1
Taxonomy:
It is study which helps to define groups of organisms according to their shared characteristics, and then assign names to those groups.
Every group of the organism(s) is assigned a position which can be added up to create a super group of a higher order. In this way, a hierarchy comes into existence. The groups which are created are known as taxa.
It can also be referred as a field of science which includes description, recognition, nomenclature and classification of organisms.
It is extensively practiced by biologists (known as taxonomists) to form groups of organisms and to segregate them according to their features and habits. The taxonomists have made the biological study of living organisms much easier by forming different groups. Taxonomy has great significance in biodiversity and conversation which are main fields of applied biology.
Taxonomy is considered as the world’s oldest profession; man started giving names to the living things in his surroundings since the time he learned to communicate.

-
2
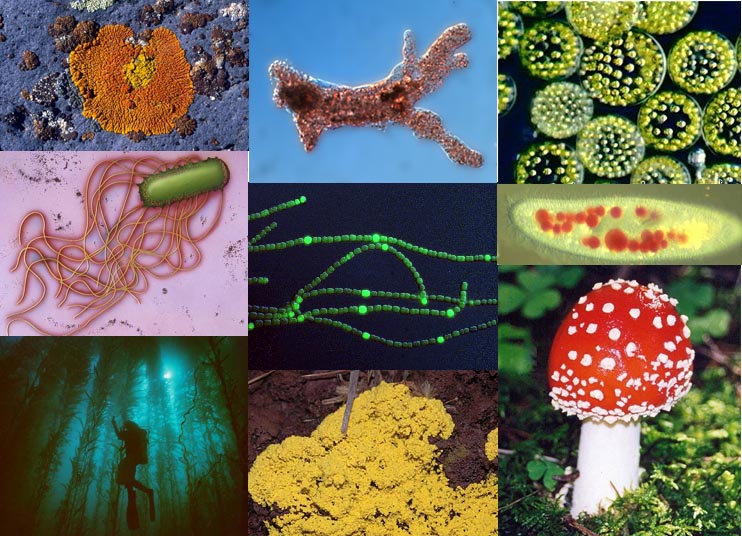
Systematics:
It is a biological study which diversifies the living organisms of past and present, and their relationships through time. The relationships amongst the living things are pictured as phylogenetic trees (commonly known as evolutionary trees, cladograms or phylogenies).
An evolutionary tree is further divided into two parts. First part is known as branching order which shows the relationships of the organisms within a group. Second part in called as branch length which identifies the period of evolution, through which the organisms have passed.
Besides, the evolutionary tree of species and higher taxa is used to understand the evolution of traits and the bio geography of the organisms.