Difference Between Throughput and Bandwidth
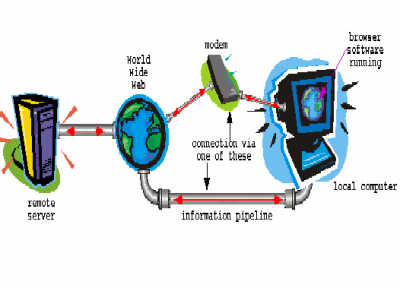
In communication networks, we often come across two very fundamental concepts which are bandwidth and throughput. These are most often applied in business scenarios where the Internet Service Providing companies (ISPs) either plan to set up new networks or are managing existing networks. Though both of these are measured in same units as these are closely related concepts, but there is a great difference between the two.
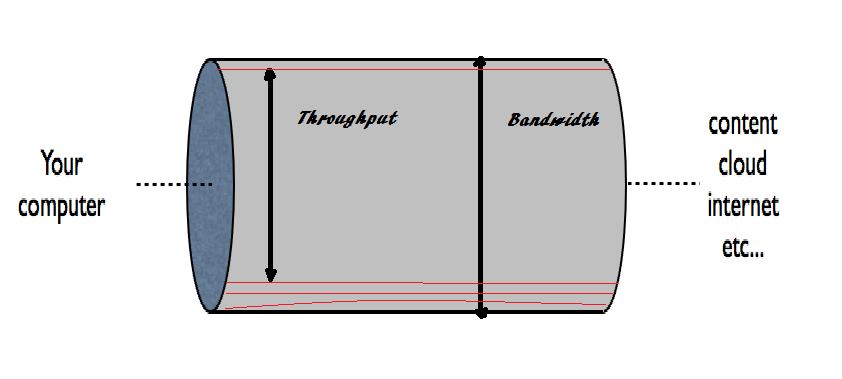
In order to understand the difference with the help of an analogy. Consider a pipeline through which water passes. Now this pipe is analogous to the communication channel and the data is analogous to water. The width of the pipe is the bandwidth. If the pipe is having some grubby layers of mud inside it, it will leave lesser room for the water to pass through it. This is the actual width of the pipe which is analogous to throughput. In other words, the available width of the pipe under use will be less then the actual width of the pipe.
Now let’s take an example from the real world. Almost every one of us downloads files from the internet. During this downloading period, a message box appears in which you are informed about the amount of file which has been downloaded so far and the remaining part of the file that is left. In addition to this, it also tells the rate at which the file is being downloaded. This mentioned rate is the ideal rate and it is the bandwidth. However it is important to note that the actual rate is different from this mentioned rate. This is because many 0ther tasks are also being executed in parallel.
So here, bandwidth is the maximum available rate at which you can download a file in an ideal situation while throughput is the actual rate at which you are downloading the file in a given time. Noise, collision and bad quality cables are some of the reasons that set the theoretical value different from the actual one.
Instructions
-
1
Bandwidth
Bandwidth is the ideal rate at which the bits of data can travel through the communication channel. It is the theoretical value and can also be called maximum throughput.
Image Courtesy: web.cs.dal.ca
-
2
Throughput
On the other hand throughput is defined as the actual data in the form of bits that travels successfully through a communication channel to the network terminal.
Image Courtesy: personal.psu.edu