Difference Between Transcription and Translation in DNA
Transcription is responsible for producing RNA molecule which is compulsory for the DNA strand. In contrast, translation fabricates the peptide string which is essential for the RNA.
DNA is parental strand for transcription and primary transcript i.e. RNA for translation. Furthermore, transcription is controlled by internal systems which are made of operon mechanisms and chromatin arrangement that contains histones and DNA methylation in eukaryotes. Besides, the operon rule entails promoter series and suppressors that are found in the main sequence. On the contrary, translational rule is made from the binding system of ribosomal subunits in the compound.
The transcriptional product goes through dicing and splicing events which remove the introns (intragenic segments). It is to be noted that the introns are non-coding in nature. Whereas, post translation changes are primarily related to chemicals which attach functional sets to the peptide arrangement.
In addition to a single RNA polymerase, three more enzymes work in the eukaryotes and help to carry out and control the transcription in prokaryotes. On the contrary, the translation process needs several different enzymes and factors for control. The process is completed in three distinct steps (initiation, elongation and termination) and each step needs a group of RNAs, enzymes and cofactors.
The enzymes and factors work in the nucleus for the process of transcription while translation takes place in the cytoplasm right after the initial RNA transcript is shifted from the nucleus.
Instructions
-
1
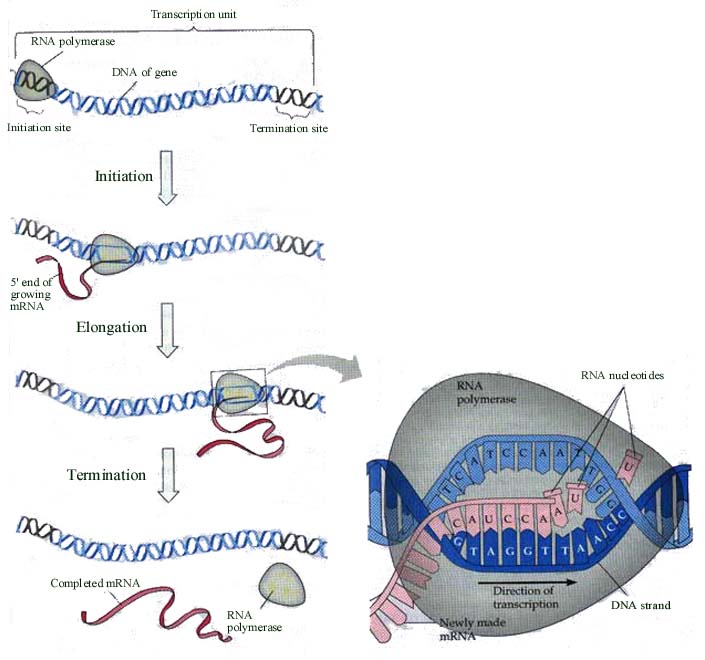
Transcription
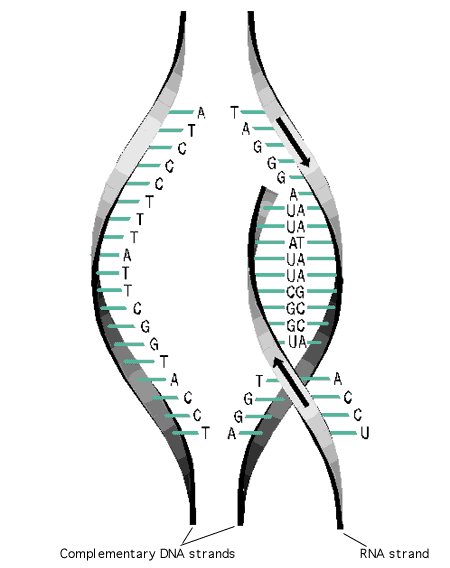
It is a process in the RNA chain is synthesised. The arrangement of RNA makes a structure which helps in the creation of proteins. In transcription, the complementary bases are connected with the DNA series which in turn are attached with the bonds of phosphoric acid that form the RNA. The chain of RNA which is formed contains nucleotides with ribosugars.
The sequence which is made after the process of transcription is known as coding strand which is compulsory to create antisense strand or template for further advancement.
-
2
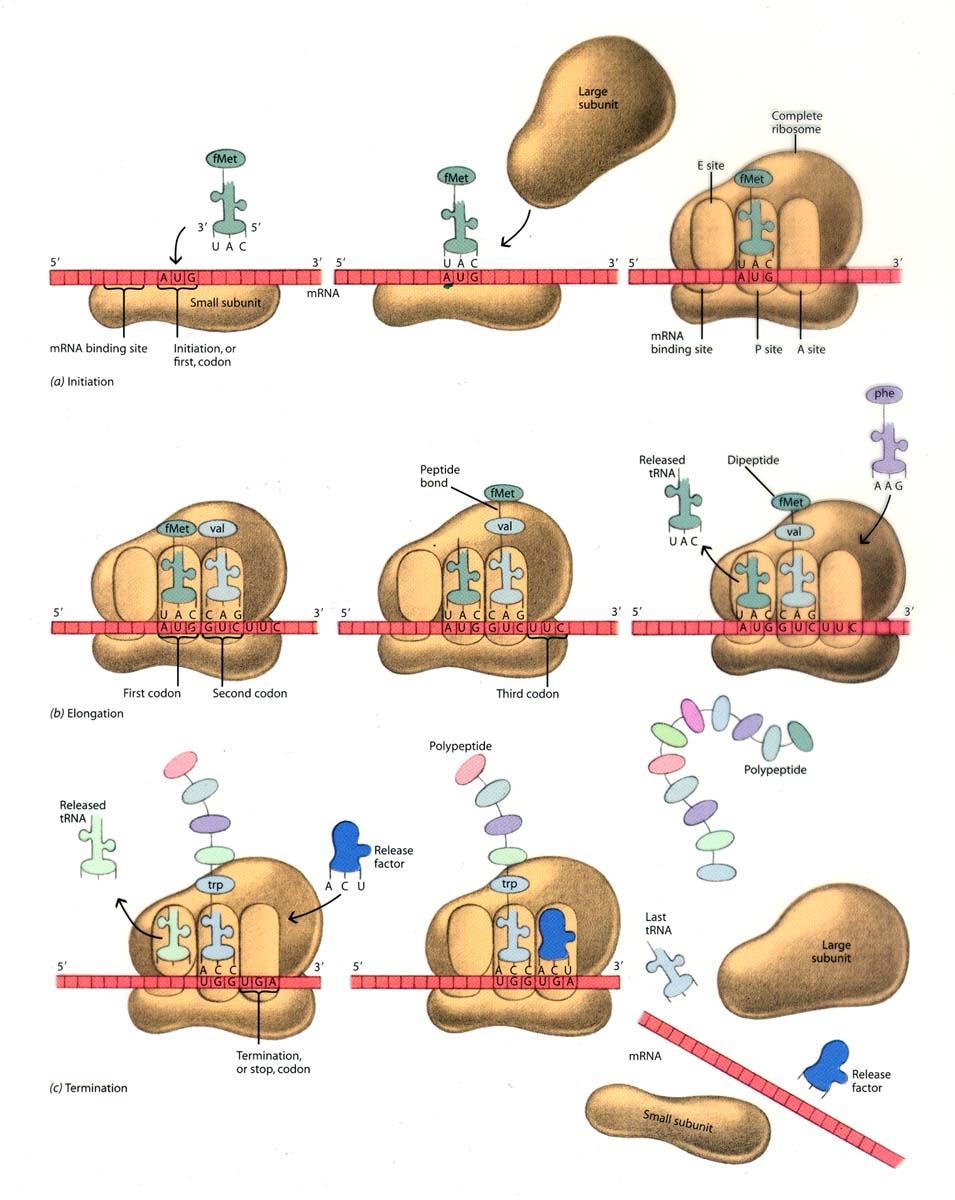
Translation
It is a process which starts after the completion of the transcription event. The primary transcript which is created in transcription is translated into an arrangement of matching amino acids which form a chain of peptide. The chain of peptide is later processed into fully functional proteins. Different kinds of enzymes help to complete the process of translation and to speed up the formation of protein through RNAs.