Difference Between Transitive and Intransitive Verbs
Verb is one of the most important parts of speech in the morphological system, indicating the state of the object or action that develops over time. All participles are formed from verbs as they represent a sign of the object by the action.
Verb as a part of speech has some morphological characteristics. These are: the form imperfect or perfect, conjugation, transition or intransitive and reflexivity. Thus, verb form carries rules and possible options for changing the verb and they can be divided into several classes and types according to the form. The first class consists of infinitives, participles, and the second- participles.
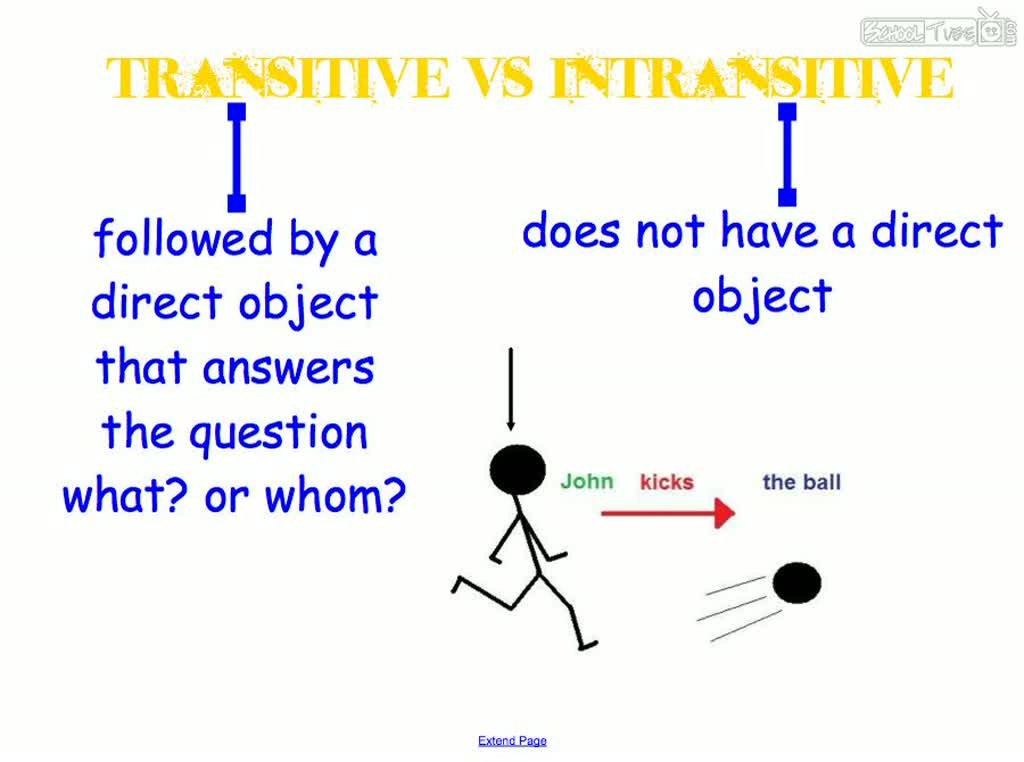
Before checking the verb starts with the category of transitivity / intransitivity. Transitive verbs denote action directed at an object, and combine with nouns in the accusative without a preposition. For example, “prick Wood” (chop – a transitive verb, as combined with a noun in the accusative case without a preposition). Intransitive verbs mean action without passing an object and they are combined with other nouns in the oblique cases. For example: “to suffer Asthma” (suffer – intransitive verb, as combined with a noun in the instrumental case).
Verbs in the English literature are divided into transitive and intransitive. If the action of the subject becomes an object, it is a transitive verb (“I eat an orange”) – if not, it is an intransitive verb (“I sleep”). Verbs in the active voice are used when we are primarily interested in the subject (“The sun illuminates the Earth”). The passive voice is used in the opposite case, when the speaker is more interested in the object (“Land of the sunlight”).
Transitional / intransitive – verbal category expresses the relationship between the subject (those who commit the act) and the object (the one to whom the action is directed). Intransitive verb indicate an action that is not transferred to the object, and thus far cannot carry a direct object. Transitional / intransitive verb is closely linked to its lexical meaning: one meaning of the verb can be transitive and the other – intransitive.
Instructions
-
1
Transitive verbs:
Transitive verbs govern the accusative form of the noun without an excuse (read a book , tell a story). -
2
Intransitive verbs:
Intransitive are not compatible with this form. Reflexive verbs contain a special kind of intransitive verbs, denoting action. Speaking of reflexive verbs, it should be noted that this category is associated with transient / intransitive.







