How to Balance Chemical Equations
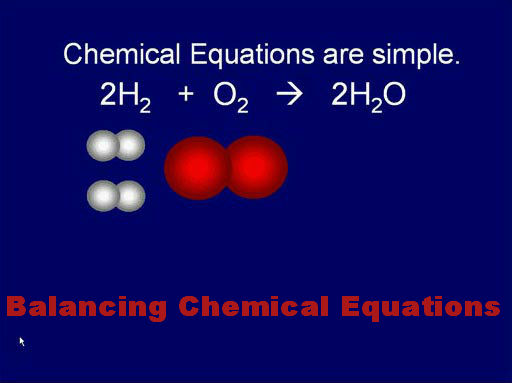
While preparing for the chemistry exam, something that proves to be irritating for all of us is practicing to balance the chemical equations. The whole book of chemistry would have been easier to memorize but the chemical equations are always a thorn in the flesh. No matter how much and how well you practice, but still you are worried about committing a mistake if there is a question on balancing the chemical equations in exam. This often makes us think that chemistry could have been the best of all science subjects had there been no chemical equations. Somehow, there is no such possibility but there are a few tips that can help you with the problem of balancing equations.
Instructions
-
1
First of all, you should be well aware of the symbols of elements and chemical formulas as it will not be possible to have a good grip without having this basic knowledge.
-
2
Make sure that you are aware of the reactants involved in a certain chemical reaction and the products that are formed as a result with their basic atomic and molecular representation.
-
3
While making a chemical equation, begin with writing unbalanced equation first with the reactants on the left side and the products on the right side of the arrow.
CaCO3 + HCL ------------------------------- CaCl2 + H20 + CO2 -
4
After you have written the unbalanced chemical equation, observe that the number of atoms and molecules at the left should be equal to those at the right.
-
5
Concentrate on the coefficients so as to ensure that the number of atoms of the element is the same on each side of the equation. If not then you have to change the coefficients to make proper formulas or symbols.
CaCO3 + HCL ------------------------------- CaCl2 + H2O + CO2 -
6
Remember that besides knowing the chemical formulas and atomic symbols, you should be aware of the results the chemical reactions like acid-base reaction, acid-metal reaction and acid-carbonate reaction.
-
7
Keep in mind that acid-base reaction results in a salt and water, acid-metal reaction results in liberation of hydrogen gas and acid-carbonate reaction results in liberation of carbon dioxide gas and water.
Na2CO3 + 2HCL -------------------------------- 2NaCl + H2O + CO2 (acid-carbonate reaction)
NaOH + HCL-------------------------------------- NaCl + H20 (acid-base reaction)
2Al + 6HCl ---------------------------------------- 2AlCl3 + 3H2 (acid-metal reaction)





