How to Test For Pheochromocytoma
Pheochromocytoma is characterized by excess production of epinephrine and norepinephrinе, brought on by growth formation(s) in one or both adrеnal glands.
There are many symptoms of symptoms of Pheochromocytoma, an increase in blood pressure being the most significant one. If you feel that you are suffering from pheochromocytoma, then you should contact your doctor right away and ask for different tests which can be done to diagnose this disease.
Instructions
-
1
First of all, you should know the symptoms that you need to report to your doctor. With the growth of tumour, the symptoms also increase in frequency and severity.
Abdominal pain, chest pain, irritability, nervousness, pallor, palpitations, rapid heart rate, severe headache, sweating, weight loss, hand tremor, high blood pressure and sleeping difficulty are some of the most common symptoms of pheochromocytoma. -
2
Get your blood pressure, heart rate, pulse and body temperature measured properly. Also, you should be prepared for a blood glucose test, which you will need to get the amount of sugar in your bloodstream measured. This test involves drawing a small amount of blood, either from the inside of your elbow, the back of your hand or the tip of your index finger.
-
3
A test will be performed to check for your body's volume of catecholamine, the class of hormones produced by the adrenal glands. These include epinephrine (formerly known as adrenalin), norepinephrine and dopamine.
-
4
You will be required to undergo a 24-hour urine test. For this test, you'll be asked to urinate in a special container at home, over a 24-hour period. This test measures catecholamine, as well as their by-products, known as catecholamine metabolites.
-
5
Prepare to have an MIBG nuclear scan of the abdomen. This test scans for possible tumours by tracing the path of an injected radioisotope (radioactive material) which shows up on certain tissues, specific to pheochromocytomas. Note that this test takes one to two hours to complete and may need to be repeated several times.
-
6
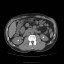
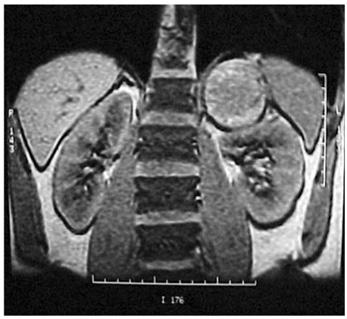
Additional imaging tests may follow, including MRI and CT of the abdomen.