How to Use Multidimensional Arrays in C++
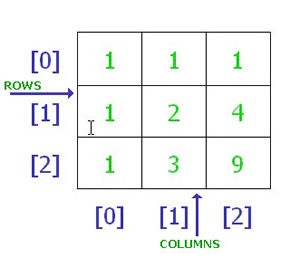
Arrays have significant importance in any programming language and they are used to build longer and bigger types of data structures containing same elements in all entries. I have written a guide on single dimensional arrays in C++ and it can be found here. Unlike single dimensional arrays multidimensional arrays are tricky to handle as in this case we need to handle multiple indexes. A multidimensional array can be seen as a table consisting of multiple rows and columns. Here in this guide I will describe the basic functionality of multidimensional arrays and how you can use them in C++.
Instructions
-
1
Multidimensional arrays look like a table as you can see in the figure. And they can hold more values as compared to a finite single dimensional array. Say we have 5 rows and 5 columns of an array then overall we will have 5*5=25 elements in that array. So first of all I will show you how to declare a multidimensional array.
Declaring a multidimensional array:
To initialize a multidimensional array the syntax used is:
Type Name [rows][columns]
For example to declare an int type multidimensional array we have to declare it like as shown below:
int multiArr [3] [3];
Above line of code will create an entry of a multidimensional array in memory with 3 rows and 3 columns consisting of 9 elements.
-
2
Initializing a 2D array in C++:
You can initialize the values of all the elements of a 2D array in C++; if you do not initialize the values then they will be garbage at start. You can initialize each row using curly brackets as shown below.
int multiArr[3][3] = {{2, 5, 9},
{4, 7, 7},
{2, 12,15}
};
This way you can initialize array of any size.
-
3
Accessing the Values of a 2D array:
To access value of a specific entry in a 2D array, you need to use two indexes, one for row and one for column e.g. you want to access the value present in row 2 and in column 3. You will do this by using following line of code:
Int temp = multiArr[1][2];
Remember that the indexes always start with 0, so in order to access row 2, you have to use index 1.
If you want to access all the entries of a multidimensional array, then you can use nested for loops.
-
4
Example code:
Following is the example of 2D array, and it will use all of the techniques mentioned above.
# include
using namespace std;
int main( ) {
int arr[3][3] = {{2, 5, 9},
{4, 7, 7},
{2, 12,15}
};
for(int i=0;i<3;i++){
for(int j=0;j<3;j++){
cout<<”value at ”<
}
}
return 0;
}
The above lines of code are initializing a multidimensional array, and then the values are accessed using a nested for loop and then these values are displayed on the terminal.







