What Are Physical and Chemical Properties of Atoms
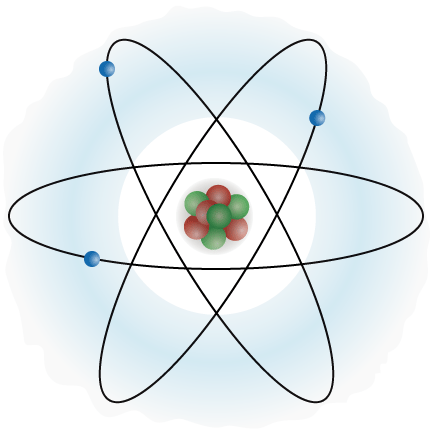
An atom is the smallest unit of matter which keeps it chemical properties. The chemical and physical properties of matter determine the behaviour of the element it forms, and the mechanics of material can be altered significantly by varying the properties of this basic unit.
Atom is made up of many small particles, but three of the main ones are neutron, proton and electron. Proton and neutron form the core of the nucleus, around which the electron revolves in orbits, the number of which can be altered and varies from atom to atom. The electron is negatively charged and about 2000 times lighter than the proton and neutron.
Instructions
-
1
Physical properties of atoms
- Atomic number is the number of proton in the nucleus of an atom.
- Atomic mass is the number of protons and neutrons in the nucleus of an atom. It specifies the mass of an atom and is expressed in atomic mass unit (amu).
The above two are the basic physical properties of atoms. These properties can influence a lot other physical properties in a molecule or an element like density, boiling and melting points, atomic radius etc. -
2
Chemical properties of atom
- Electronegativity is the capability of an atom to attract a single or a cloud of electrons towards itself.
- Energy of ionization indicates the amount of energy required to remove an electron from a free atom in a vacuum. The first energy of ionization is the amount of energy required to remove a single electron from the outer orbit. There can be up to five energy of ionizations.
- Standard potential indicates the potential indication for a reduction-oxidation reaction. The equilibrium potential is zero. When this potential is greater than zero, oxidation reaction occurs and reduction occurs when the potential is less than zero.
- Electronic shells represent the distribution of electrons in the orbits around the nucleus. Electrons revolve around the nucleus in circular orbits, each possessing a certain level of energy. These energies usually increase as we move away from the nucleus.
- Isotopes are the atoms of the same element that have the same atomic number, but different atomic masses. This is because of the varying number of neutrons in the nucleus of such atoms.