What is Adrenaline and How Does It Work
Adrenaline is an enzyme produced by the adrenal glands under high octane and stressful situations. Also known as epinephrine, it is the basic building block of human body’s acute stress response system, also called the “fight or flight” response.
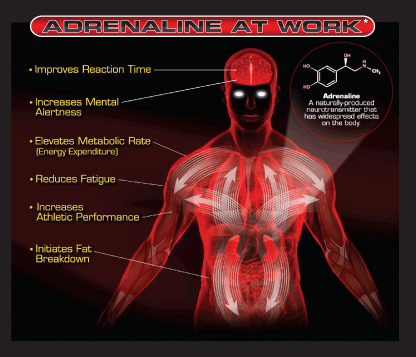
The basic body response after the release of adrenaline involves the stimulation of the heart rate, contraction of the blood vessels and dilation of the air passages, which means that there is a significant increase in the supply of blood to the muscles and the provision of oxygen to the brain, making the human more animated and agile.
Adrenaline is not only used to increase the activity, it can also be used in the cure of various diseases and is being used by doctor and pharmaceutical companies all across the globe. It is basically driven from an amino acid, tyrosine and form the basis of human self defence system.
Instructions
-
1
Fight or flight response
Whenever a person is in trouble, physical or mental, there are only two ways to counter it. Either you hang tough and fight the issue out, or escape the situation. Both these things require energy, which is proportionately higher than what we have under normal circumstances.
This added energy is provided by adrenaline, which increase the stimulation rate of the body.
For example, when you experience a physical danger in the form of a scuffle, body’s reactive system to this stressful situation demands the production of adrenaline – commonly known as "adrenaline rush” – and all of a sudden you will feel increased strength, quickness and mental awareness.
Similarly, you will never be able to run faster than in the situation where an aggressive dog is trailing you. The added speed is the result of the adrenaline rush. -
2
Medical application
Adrenaline is used in the treatment of anaphylaxis, also known as anaphylactic shock. It is also used in the treatment of people having severe allergic reactions and can be administered in the form of injections. Adrenaline shots are also administered to recover people in case the heart rate falls to zero, and can also be used to prevent cardiac arrest.