What Is Nuclear Fusion And Fission
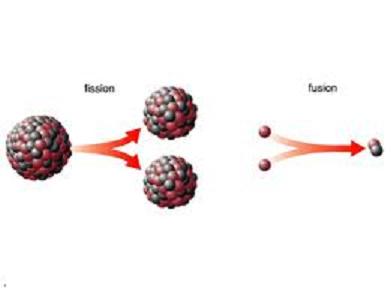
Nuclear physics is a very interesting subject and has become even more popular among the younger generation as they are aware of the impact that it can make on the balance of power and the threat it poses to global security. While nuclear physics is a comprehensive and very complicated subject, it basically revolves around two key reactions, nuclear fission and nuclear fusion. The two reactions may look very simple at first, but as you go into their detail, you will come to realise that they are extremely complicated and, if successfully initiated, extremely useful (nuclear energy) and, in some cases, devastating (atomic and hydrogen bomb) reactions.
Instructions
-
1
Nuclear fission is an energy-releasing reaction that involves the splitting of the nucleus of an atom into smaller sub-atomic particles, whereas nuclear fusion is an energy-releasing reaction that involves the fusion of two or more atoms to form a larger or heavier atom.
-
2
Fission reactions are only performed artificially, i.e. through human involvement, whereas fusion reactions occur in nature. Two biggest examples of natural occurrence of nuclear fusion are the sun and the stars, where the reaction continues to yield energy on its own without any kind of human involvement.
-
3
A fission reaction produces a large amount of radioactive particles, whereas a fusion reaction produces only a small amount of radioactive particles. In case a fission “trigger” is used to initiate the fusion reaction, then the number of radioactive particles produced will be significantly higher than the number of radioactive particles produced by normal fusion reaction.
-
4
In order to perform a nuclear fission reaction, high-speed neutrons and critical mass of the substance is required. However, nuclear fusion reaction requires high density and an environment with high temperature.
-
5
The amount of energy required to perform a fission reaction is significantly lower than the amount of energy that is required to perform a fusion reaction. Splitting a large atom into two or more smaller atoms is fairly more convenient in terms of energy requirement. However, combining two or more smaller atoms to form a large atom requires overcoming the electrostatic repulsion, which consequently results in the requirement of greater energy. This energy is clearly not an issue on the sun and the stars, where the fusion reaction continuously takes place.
-
6
While the amount of energy released by nuclear fission is almost a million times greater than the energy released in chemical reactions, it is still three-to-four times less than the amount of energy that is released by nuclear fusion.
-
7
Nuclear fission allowed the scientists to develop an atomic bomb, where nuclear fission triggered by nuclear fission allowed scientists to develop the hydrogen bomb.






