What is The Difference between Propane and Butane
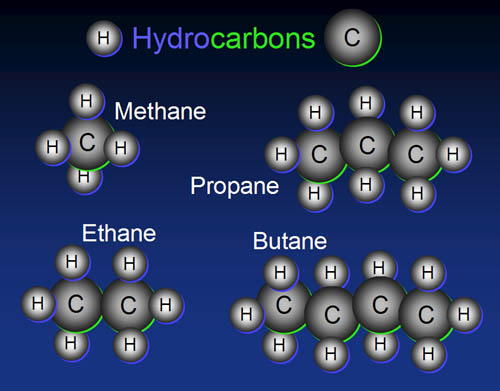
Both propane and butane are straight chain hydrocarbons in which each carbon atom is attached to the other through a single bond. Both of them are gases and share many other similar qualities and applications. Both propane and butane are extracted from petroleum, as natural gas, but they can also be compressed to liquid form by applying high pressure and reducing the temperature. They both are used as fuel for heating vehicle engines as well as industrial and household equipment. When combusted in the presence of air, each produces similar by-products – carbon dioxide and water vapours. When burnt in the presence of limited amount of oxygen, carbon monoxide and soot are also produced alongside carbon dioxide and water.
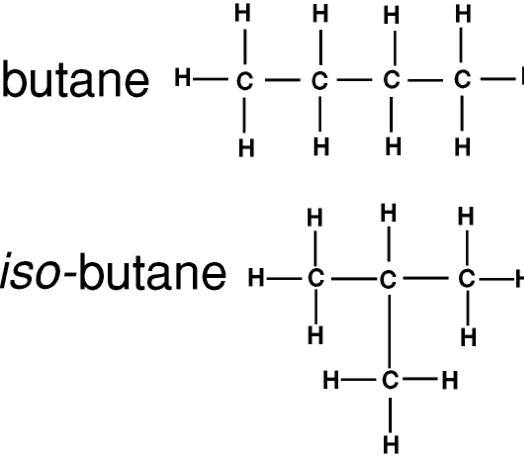
Besides these similarities, these two organic compounds have almost as many differences as well. The basic difference between the two is their structural formula. Propane contains three carbon atoms attached together through single bond, while butane contains four carbon atoms also attached to form a straight chain. The former cannot be branched, while latter has a branched isomer, commonly known as isobutane. Isobutane or methylpropane is the simplest alkane containing tertiary carbon. Butane is cheap, burns cleanly and provides more energy (49.50 MJ/Kg) as compared to propane (46.44 MJ/Kg). However, the latter is preferred in situations where temperatures are expected to drop below freezing point.
Instructions
-
1
Propane
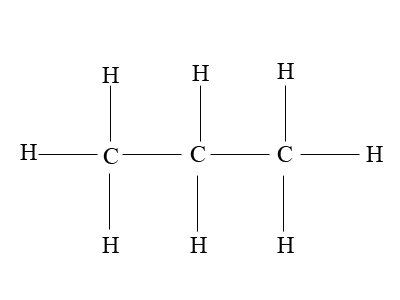
Propane is a straight-chain alkane containing three carbon atoms and eight hydrogen items. It has a chemical formula of C3H8, and is normally a gas; however, by applying high pressure, it can be compressed to a transportable liquid (LPG). Propane is obtained as a by-product during petroleum refining and is commonly used for heating and as a fuel for vehicle engines and portable stoves. The energy density of propane is 46.44 MJ/Kg. Propane has low boiling point (-42 degrees Celsius) and can be stored in gaseous form in high pressure tanks (two to three thousand PSI). These characteristics make it an ideal choice for hostile environments.
Read more: How to Use a Digital Manometer to Check Gas Pressure on a Propane
-
2
Butane
Butane is a straight chain hydrocarbon with the chemical formula C4H10, containing four carbon items and ten hydrogen atoms. It is a gas at room temperature and normal air pressure, but can be compressed to liquid at low temperature and high pressure. It is mainly used as a fuel gas for gasoline blending and is a key ingredient in the manufacturing of synthetic rubber. It is also blended with propane and other hydrocarbons at higher pressure to form a liquefied petroleum gas, LPG, used as a fuel for vehicles.
Related: How to Store Butane for a Lighter